
Vegan Cosmetics Market Growth and Development Insight -...
The Global Vegan Cosmetics Market size was valued at USD 17 Billion in 2022...
-

The Global Vegan Cosmetics Market size was valued at USD 17 Billion in 2022...
DXB APPS, a top mobile app development company in UAE focuses on the techni...

Find the importance of air duct and vent repair in Waxahachie to improve yo...

If your law firm is not appearing in these search results, you may lose out...

Discover why the best Digital Marketing Company in Dwarka is essential for...
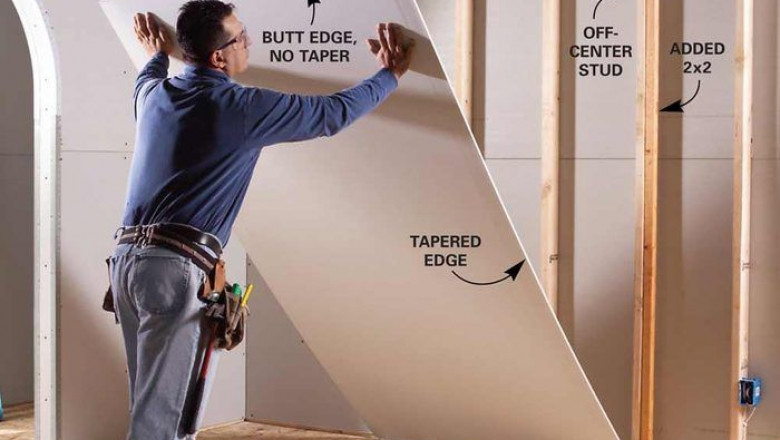

Top Residential Drywall Contractors in Kansas City, MO – Precision You Can...

One big difference between SEO for law firms and other industries is the st...

Prepare for the CS0-003 exam with this comprehensive guide to the CompTIA C...











